Pigments that are naturally found in the skin
- The presence of several chromophores affects skin color
- The most significant pigment is melanin, which is produced by melanocytes
Pigments that are naturally found in the skin

Genetic factors determine the amount of melanin in the skin; those with more melanocytes typically have darker skin, while those with fewer melanocytes usually have lighter skin. In addition, numerous factors, such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, skin traumas, and specific medical diseases, can impact this skin condition.
Sometimes pigments that are ordinarily absent from the skin develop and change the skin color.
These pigments could be:
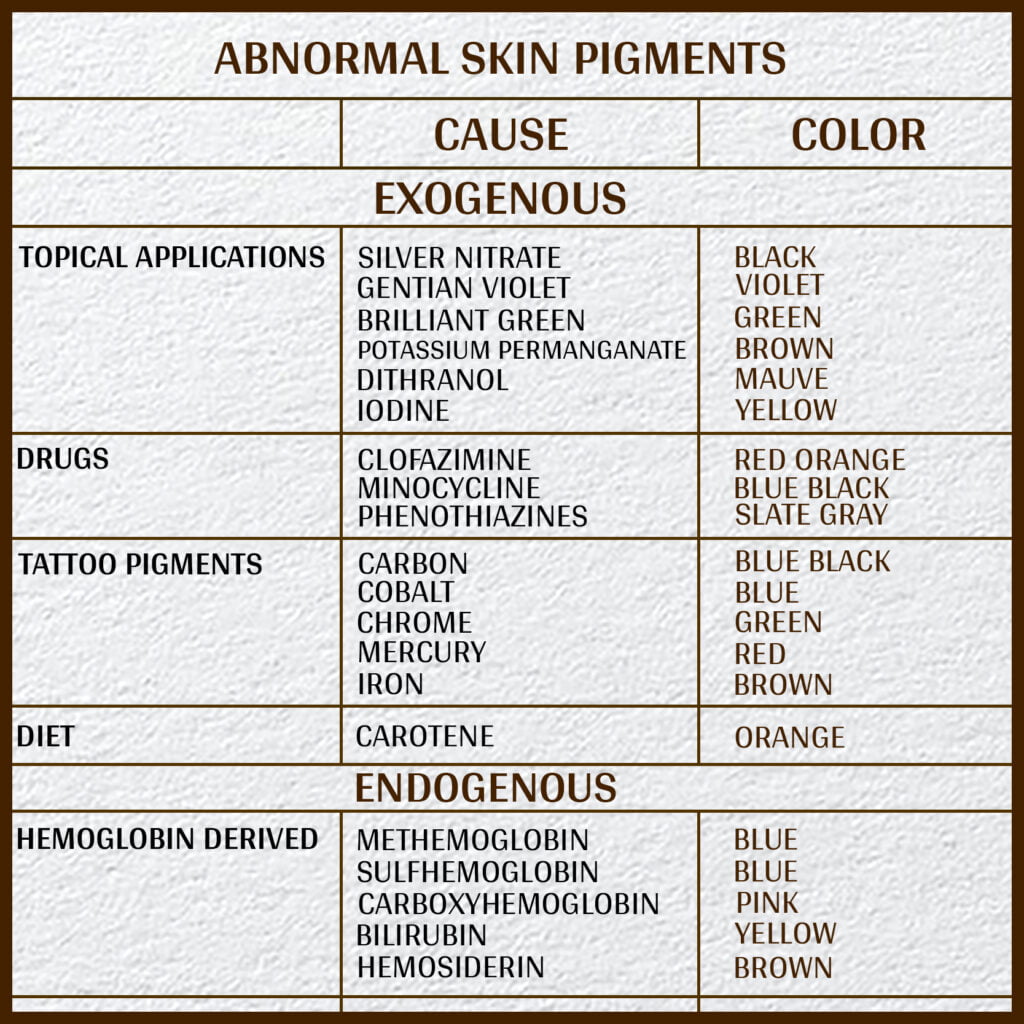
These diseases cause the skin to produce either too little or too much melanin, affecting the skin’s color. A few common disorders that develop from changes in melanin production are as follows.
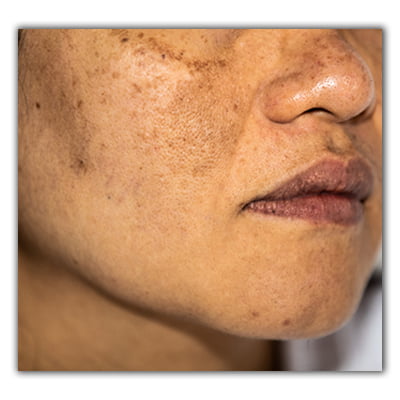
Hyperpigmentation (dark spots)
Hypopigmentation (light spots)
III. Depigmentation (white spots or patches)
Multiple forms of this disorder exist, including:
Solar Lentigines. Sun spots, liver spots, and age spots are all terms used to describe solar lentigines. They are tiny, black spots that develop on the skin after exposure to the sun. People above the age of 50 are more likely to develop solar lentigines.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). It appears after an injury to the skin, such as acne or a skin infection. Additionally, PIH might develop after specific medical procedures like laser therapy or chemical peels.
Melasma. It primarily affects women, especially during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills. Brown or gray-brown patches appear on the face due to the disorder, most prominently on the cheekbones, forehead, nose, and upper lip.
Freckles. An increase in melanin production causes small, flat patches known as freckles to form on the skin. They are more prevalent in those with fair complexion, typically tan or light brown.
Treatment:- Although this condition tends to be harmless, some people may want to remove or lessen it. To minimize the impact, especially in people more susceptible to the condition, it’s important to wear sunscreen and spend as little time in the sun as possible.
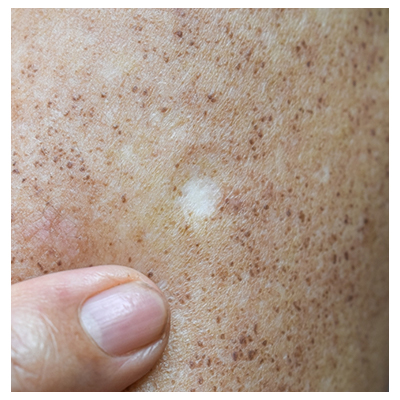
It is when the skin generates insufficient melanin, leaving lighter patches or spots on the skin.
Multiple forms of this disorder exist, including:
Vitiligo. A skin condition known as vitiligo causes the melanocytes to be attacked by the immune system, resulting in skin color loss. White skin patches that can occur anywhere on the body can result from this. Vitiligo is not genetic and develops later after birth. Herein, leucotricha signifies a condition where the roots and, occasionally, the entire hair strands turn white in this context.
Albinism. It is a genetic condition that causes skin, hair, and eyes to have less or no melanin. People with albinism are more sensitive to sunlight and have light skin, hair, and eyes.
Tinea versicolor. Tinea versicolor is a fungus that can affect the skin and result in hypo- or hyperpigmentation. The chest, back, and arms often appear as white or light brown spots.
Pityriasis alba. It is a prevalent skin disorder that primarily affects children and produces hypopigmentation. The face, neck, and arms have light-colored patches as a result.
Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis. It is a disorder that results in tiny, white spots on the skin, most frequently on the arms and legs. Older persons with pale skin are more likely to develop this condition, despite the fact that there is no recognized cause for it.
Treatment:- The underlying cause of this issue will determine the best course of treatment. Albinism cannot be treated; however, people with it should take measures to shield their skin from the sun, such as applying sunscreen and wearing protective clothing. Antifungal drugs can be used to treat tinea versicolor. Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis and pityriasis alba go away on their own without medical intervention.
Prevention:-
Individuals with this condition should protect their skin from the sun and address the underlying problem. Sunscreen and protective clothing can help stop future skin deterioration and may help make the condition look better.
This skin condition develops when the melanin pigment dramatically decreases, which can cause the human skin to lose its original color. Such a loss of pigment can be temporary or permanent, with a loss of either entire or partial melanin pigment.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation
Numerous factors can contribute to this condition, including:

Each patient’s medication is explicitly tailored to their needs, considering their mental makeup, physical symptoms, and other personal characteristics. In addition to the medical diagnostics and requirements, age, occupation, prior illnesses, and living circumstances specific to that individual are also considered while treating a long-term disease. After choosing the right medication, the team of doctors pays complete attention to the dosage, frequency, and potency that would produce the best results and accelerate healing in each case. Driven by values of compassion, integrity, and ethical practices, we have a history of recovering thousands of patients successfully.
Committed to providing healthcare that’s affordable and accessible to all.